Searching for more information about your personal risk for HIV infection? If you’re in New York’s Hudson Valley region, talk to our Regional Prevention Initiative about testing, individual counseling sessions or information sessions near you.
Against All Odds
by Trenton Straube
Playing the HIV numbers game is less—and more—risky than you think. Originally published in POZ Magazine, April 2014.
Can you get HIV from oral sex? That’s probably one of the most common questions AIDS service providers and doctors get asked. Americans really want to know their HIV risk during fellatio—even more so than during anal sex. Sure, you can Google the subject, but the results may further confuse and scare you.
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) fact sheet describes the probability of oral sex transmission as “low.” But what does that mean? The AIDS.gov website puts it this way: “You can get HIV by performing oral sex on your male partner, although the risk is not as great as it is with unprotected anal or vaginal sex.” Regarding going down on a woman, the site explains: “HIV has been found in vaginal secretions, so there is a risk of contracting HIV from this activity.”
Does this put your mind at ease? Hardly. That’s why many of us seek out percentages and ratios when we talk about risk. Numbers seem less abstract, more specific. But do they give us a better understanding of HIV risk and sexual health? Let’s do the math.
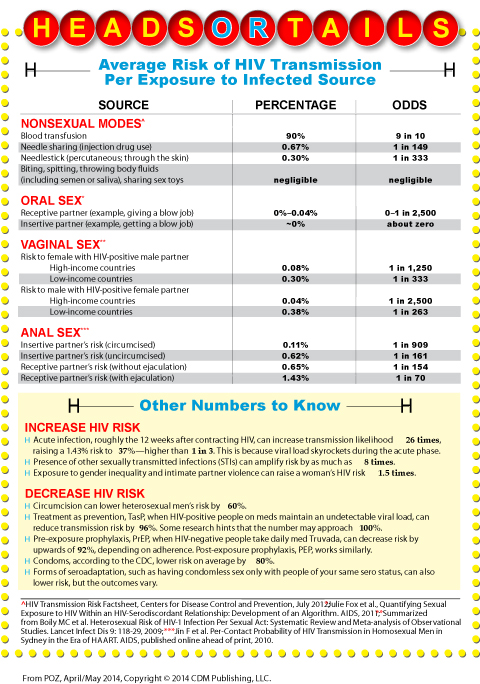
Probabilities of HIV transmission per exposure to the virus are usually expressed in percentages or as odds (see chart at the end of this article). For example, the average risk of contracting HIV through sharing a needle one time with an HIV-positive drug user is 0.67 percent, which can also be stated as 1 in 149 or, using the ratios the CDC prefers, 67 out of 10,000 exposures. The risk from giving a blowjob to an HIV-positive man not on treatment is at most 1 in 2,500 (or 0.04 percent per act). The risk of contracting HIV during vaginal penetration, for a woman in the United States, is 1 per 1,250 exposures (or 0.08 percent); for the man in that scenario, it’s 1 per 2,500 exposures (0.04 percent, which is the same as performing fellatio).
As for anal sex, the most risky sex act in terms of HIV transmission, if an HIV-negative top—the insertive partner—and an HIV-positive bottom have unprotected sex, the chances of the top contracting the virus from a single encounter are 1 in 909 (or 0.11 percent) if he’s circumcised and 1 in 161 (or 0.62 percent) if he’s uncircumcised. And if an HIV-negative person bottoms for an HIV-positive top who doesn’t use any protection but does ejaculate inside, the chances of HIV transmission are, on average, less than 2 percent. Specifically, it is 1.43 percent, or 1 out of 70. If the guy pulls out before ejaculation, then the odds are 1 out of 154.
Say what? Is HIV really this hard to transmit, especially in light of the alarming statistics we are bombarded with? Although the CDC estimates that nearly 1.1 million Americans are living with HIV and that the rate of new infections remains stable at about 50,000 per year, there has been a 12 percent increase between 2008 and 2010 among men who have sex with men (MSM)—including a 22 percent jump among young MSM ages 13 to 24.
A report by the Black AIDS Institute states that African-American same-gender-loving men have a 25 percent chance (which is one in four odds) of contracting HIV by the time they’re 25 years old—and a 60 percent chance by the time they’re 40. Other researchers have predicted that half of all gay men in America who are 22 years old today will be HIV positive by the time they’re 50.
So how do we go from the odds being 1 out of 70 that HIV will be transmitted during the most risky sex act to the odds being 1 out of 2 that young gay men in the United States will contract HIV before they’re 50? (And before you even think it: No, the answer is not that everyone with HIV is a ginormous slut who has never heard of safer sex.)
For starters, you have to understand that these probabilities of HIV transmission per single exposure are averages. They are general ballpark figures that do not reflect the many factors that can raise and lower risk.
One such factor is acute infection, the period of six to 12 weeks after contracting the virus. At this time, viral load skyrockets, increasing a person’s infectiousness by as much as 26 times (the same thing as saying “26-fold”). So right there, the per-act risk of receptive vaginal transmission jumps from 1 out of 1,250 exposures to 1 out of 50 exposures, and the risk of receptive anal sex goes from 1 out of 70 to higher than 1 out of 3. It’s also important to realize that during acute infection, the immune system has not yet created the antibodies that lower viral load, at least for a few years. HIV tests that rely on antibodies may give a false negative reading during an acute infection, also known as the “window period.”
The presence of another sexually transmitted infection (STI)—even one without symptoms, such as gonorrhea in the throat or rectum—can raise HIV risk as much as 8 times, in part because STIs increase inflammation and thus the number of white blood cells that HIV targets. Vaginal conditions such as bacterial vaginosis, dryness and menstruation also alter risk.
Other factors lower risk. Circumcision does so an average of 60 percent for heterosexual men. HIV-positive people who have an undetectable viral load thanks to their meds can reduce transmission risk by 96 percent, a concept known as “treatment as prevention.” Early results from the ongoing PARTNER study (to be completed in 2017) found zero transmissions among both straight and gay serodiscordant couples when the positive partner was on successful treatment, even if STIs were present. HIV-negative people can take a daily Truvada pill as pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, to lower their risk by 92 percent; similarly, there is post-exposure prophylaxis, or PEP. And the CDC says condoms lower risk about 80 percent. Of course, these numbers will vary based on correct and consistent use of the prevention strategy.
Researchers also view risk through the constructs of family, relationships, community and socioeconomic status. A quick example: According to CDC data, 84 percent of HIV-positive women contract the virus through heterosexual contact. As researchers including Judith Auerbach, PhD, an adjunct professor at the University of California, San Francisco point out, the phrase “heterosexual contact” masks the prevalence of anal sex among straight couples and the role of sexual violence—which can be significant because exposure to gender inequality and intimate partner violence triples a woman’s risk for STIs and increases her chance of getting HIV 1.5 times.
Then there is the concept of cumulative risk. The oft-cited numbers for the risk of HIV transmission take into account one instance of exposure. But this is not a static number. Risk accumulates through repeated exposures, though you can’t simply add up the probabilities of each exposure to score your total risk. Statisticians, in case you’re curious, do have a formula for cumulative risk: 1 – ( ( 1 – x ) ^ y ) in which x is the risk per exposure (as a decimal) and y is the number of exposures.
But let’s face it, many of us can’t tabulate the tip at a restaurant, so it’s unlikely we’ll whip out the advanced algebra during sexytime. Yet not even the Nate Silvers of the world would be wise to gauge HIV risk based on statistics. Doing so is a serious gamble. Numbers and probabilities can be miscalculated and misinterpreted.
Case in point: Having a 1 in 70 chance of transmitting HIV does not mean it takes 70 exposures to the virus in order to seroconvert. It simply means that out of 70 exposures, on average, one will lead to HIV; bad luck might have it that the transmission occurs on the very first exposure.
Another important concept to grasp is absolute risk (what the risk actually is) versus relative risk (the percent change in the risk). Phrases like “PrEP can reduce your risk by 92 percent” tell us relative risks, but most people want to know absolute risks. In this example, a 92 percent risk reduction does not mean the final absolute risk is 8 percent. Instead, it is a 92 percent reduction of the beginning risk. If the beginning absolute risk is 50 percent, then PrEP reduces the risk to 4 percent; if the beginning risk is 20 percent, then PrEP lowers it to 1.6 percent.
Armed with data like this, it’s tempting to try to calculate your HIV risk for specific scenarios and then plan accordingly. For example, what are the odds of getting HIV from someone with an acute infection if you’re on PrEP? Such exercises can be problematic, cautions James Wilton, of the Canadian AIDS Treatment Information Exchange (CATIE), who specializes in the biology of HIV transmission and its implications for HIV risk communication. In real life, because of all the variables involved—ranging from a person’s viral load to HIV’s prevalence in the community—the beginning and (therefore) final risks for each individual are very hard to pinpoint. “The numbers you come up with are not definitive,” he notes. Also, there are often research gaps, he says, meaning that in many cases, scientists might not yet have real-world examples to back up these numbers and calculations, but they do have mathematical modeling and the biological rationale for why certain ideas about HIV risk are true. For example, we don’t have direct research showing that the HIV transmission risk while on PrEP is higher if a partner has acute HIV infection. What’s more, a lot of HIV studies are conducted among serodiscordant heterosexual couples in Africa, and scientists aren’t 100 percent sure that the results apply to everyone.
“We know that there’s not a lot of certainty in these numbers,” Wilton says. But he stresses that “they can be a good tool for helping people understand risk—they just need to be packaged with a lot of information.” (For a more detailed discussion, check out Wilton’s webinars on CATIE.ca. And for a great primer on understanding health statistics, get your hands on a copy of Know Your Chances: How to See Through the Hype in Medical News, Ads, and Public Service Announcements.)
When you lack information or misunderstand facts, you can’t grasp your true HIV risk. If you underestimate the HIV prevalence in your community, you’ll underestimate your risk. Surveys have found that more than one in five gay men in urban cities are HIV positive, and the virus is more prevalent among MSM of color and certain communities. People in these communities are more likely to come in contact with the virus even if they have fewer partners and practice safer sex more often. In other words, everyone’s HIV risk is not the same.
Perhaps the biggest miscalculation is the incorrect assessment that you or your partner is HIV negative. That’s why risk-reduction strategies like serosorting (having sex without condoms only with people of your same status) have a larger margin of error.
Perry Halkitis, PhD, a New York University researcher who has followed cohorts of young MSM and older HIV-positive people, has observed that people make assumptions such as: “He’s older and from the city, so he’s more likely to be positive and I won’t sleep with him. But a young guy from the Midwest who looks negative? Sure, let’s do everything!”
“People are making decisions based on their assessment about the person, and it needs to be much more focused on the act,” says Halkitis, who also believes basic HIV education must go into the nuances of transmission. He wonders who is teaching young people not to use Vaseline with condoms, for example, or not to douche right before sex (if you must, do it a few hours earlier) or, if you’re shooting drugs, not to share the water and works, which can also spread the virus.
Data be damned. All the numbers in the world won’t change the fact that people are terrible at gauging their HIV risk. Often for good reason. If you’re struggling to find a job, a meal or a place to live, HIV is not high on your list of concerns, even if exposure to more risk in your daily life raises your risk for the virus. If you’re falling in love or dating, you don’t view your partner as an HIV threat, despite the fact that as much as two-thirds of HIV today is spread through relationships.
Even in hook-ups, people aren’t likely tabulating their HIV risk. One survey asked young MSM who cruised for sex online to list their main worries. The answers? That the person they met wouldn’t look like their profile, or that they’d be rejected by the person—or be robbed or beaten or raped. HIV wasn’t the top concern.
This isn’t because the young men were ignorant about the virus, says Columbia University’s Alex Carballo-Dieguez, PhD, one of the authors of that study, along with numerous additional MSM and HIV research. “In the interview room, sitting in front of me, most gay men have heightened risk perception and can accurately recite all the circumstances that may result in HIV transmission,” Carballo-Dieguez says. “But at the time of the sexual encounter, when men are seeking the most satisfactory experience possible, risk perception recedes and is replaced by love, trust, intimacy, lust, kinkiness and many other condiments that improve the flavor of sex. In [Blaise]Pascal’s words, Le Coeur a ses raisons que la raison ne connait point [The heart has its reasons that reason knows nothing of].”
“Our experiences of sex are not about ‘Danger! Danger! Will Robinson!’” says Jim Pickett, director of prevention advocacy and gay men’s health at the AIDS Foundation of Chicago. “Sex is about pleasure and intimacy and things that make us feel good. And in the real world, risk-takers are celebrated. We have to take risks every day.” A better approach, he says, is not to ask, “What’s my risk for HIV?” but instead to think, “What can I do to enjoy the sex that I want to have but remain free of diseases?”
Len Tooley, a colleague of Wilton’s at CATIE who also does HIV testing, agrees. Sexual health is often framed in the idea of risk instead of rewards. This may present HIV and those living with it as the worst possible outcome imaginable, he notes, which is not only stigmatizing but often irrational and false since many people with HIV are, in fact, just fine.
“When we get embroiled in concepts of risk, it’s easy to go down the rabbit hole,” Tooley says. “When people ask for numbers, they’re usually trying to find a balance between what they want to do sexually and the chances that those activities would lead to HIV transmission.” The ensuing discussions, he says, bring up questions about morals and values around HIV transmission, about how much risk we think is worth taking, how we perceive HIV as a possible result of our actions, and when it’s OK to ditch condoms. Questions, in other words, that can’t be answered with a simple number








